VPVehicleJoint #
Encapsulates a ConfigurableJoint component in a comprehensive wrapper suitable to use in multi-part and articulated vehicles. Unlike ConfigurableJoint, VPVehicleJoint may be enabled and disabled in runtime.
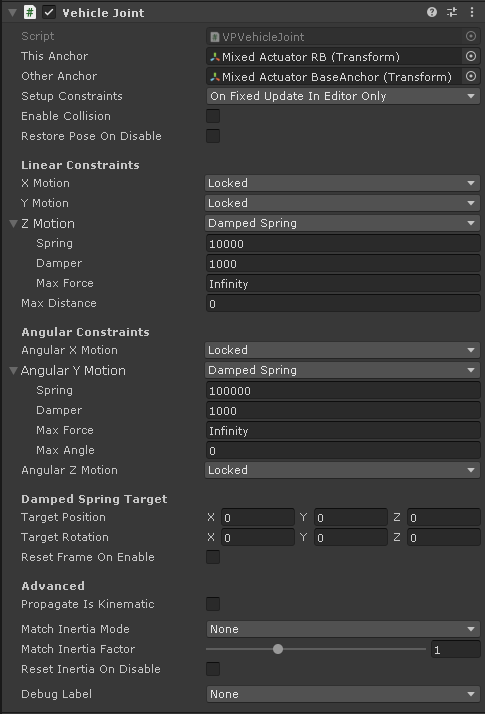
- This Anchor, Other Anchor
-
Transforms (GameObjects) belonging to the two different rigidbodies to be attached.
- This Anchor (optional): Transform in the hierarchy of the Rigidbody ("This") the VPVehicleJoint component belongs to. Uses the component's Transform if not specified.
- Other Anchor: Transform in the hierarchy of the other Rigidbody ("Other") to attach this rigidbody to.
It's expected the anchors to be in the same position (or very close) when the VPVehicleJoint component is enabled. Otherwise they may be suddenly moved by the joint constraints.
This Anchor and Other Anchor must be in the hierarchy of different Rigidbodies. These Rigidbodies may be parented or not.
- Setup Constraints
-
When to update the constraints and their parameters:
- On Enable: once when the VPVehicleJoint component is enabled.
- On Fixed Update: every physics step. Use this when the constraints or their parameters may change in runtime.
- On Fixed Update In Editor Only: Works as On Fixed Update in the editor but as On Enable in builds. Useful for fine tuning the constraints during development in the Editor, but they will be optimized on builds.
- Enable Collision
- Allows collisions between the colliders of the joined bodies.
- Restore Pose On Disable
- Restore local position and rotation of the VPVehicleJoint's transform when the component is disabled.
Linear Constraints #
Enforce the position of the anchors to be in the same world position. Constraints are local to "This" Rigidbody. Different modes may be configured per local axis:
- Locked
- Enforces the position to stay at the anchor in the given local axis.
- Free
- Position is free to move along the given local axis.
- Damped Spring
-
Enforces the position to stay at the anchor in the given local axis by applying the specified spring and damper values.
In this mode Target Position may be used to dynamically move the Rigidbody the given offset in local coordinates with respect to the anchor.
If the force required to apply the constraint exceeds Max Force then the joint breaks. Use the standard event method OnJointBreak to detect and handle broken joints.
- Max Distance
- Maximum distance the Rigidbody can move from the anchor point in Free and Damped Spring modes. 0 = unlimited.
Angular Constraints #
Enforce the local rotation of "This" Rigidbody with respect to the "Other" Rigidbody to remain constant.
- Locked
- Preserves the existing rotation between the rigidbodies around the given axis local relative to "This" Rigidbody.
- Free
- "This" Rigidbody is free to rotate around the given local axis.
- Damped Spring
-
Enforces the rotation of "This" Rigidbody relative to the "Other" Rigidbody around the given axis to stay at the value given by Target Rotation by applying the specified spring and damper values.
Modify Target Rotation to dynamically rotate "This" Rigidbody around its local axes relative to the "Other" Rigidbody.
Max Angle limits the rotation angle in the given axis from the original rotation. No effect if 0.
If the torque required to apply the constraint exceeds Max Force then the joint breaks. Use the standard event method OnJointBreak to detect and handle broken joints.
Damped Spring Target #
Used by constraints in Damped Spring mode to modify the position and/or rotation in runtime.
- Target Position
- Offset from the anchor position in coordinates local to "This" Rigidbody.
- Target Rotation
- Local rotation of "This" Rigidbody with respecto to the "Other" Rigidbody.
- Reset Frame On Enable
- Reset Target Position to 0 and Target Rotation to Identity when enabling VPVehicleJoint.
Advanced #
- Propagate Is Kinematic
- Applies the Is Kinematic flag from the "Other" Rigidbody to "This" one.
- Match Inertia Mode
-
When configured, modifies the inertia of "This" Rigidbody to be in a similar order of magnitude of the "Other" Rigidbody. This improves the joint stability when the connected masses are very different without having to increase the physics rate.
- Connected Masses: Make the magnitude of this inertia proportional to the ratio of the connected masses.
- Connected Inertia: Make the magnitude of this inertia a ratio of the magnitude of the connected inertias.
- Match Inertia Factor
- Multiply the inertia by this factor after calculating the new inertia.
- Reset Inertia On Disable
- Calls Rigidbody.ResetInertiaTensor() to restore the inertia in "This" Rigidbody when VPVehicleJoint is disabled.
- Debug Label
- Shows the reported values of the Joint in runtime as a gizmo label.