Vehicle Dynamics #
Add-on components modifying the vehicle's handling and behavior.
You can write your own add-on components easily if the provided components don't fit your needs or you need other features.
VPAntiRollBar #
Anti-roll bars (also "stabilizer bars" or "sway bars") connect the two wheels of the same axle allowing a limited degree of freedom between their suspensions. When one of the wheels is pushed upwards, the stabilizer bar transfers a portion of that compression force to the other wheel, so its suspension compress as well. This reduces the body lean in turns at that axle.
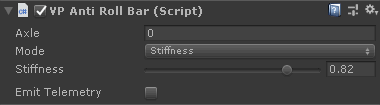
Full details on VPAntiRollBar in the Suspension section.
VPRollingFriction #
Applies rolling resistance as per the wheels rolling on the ground.
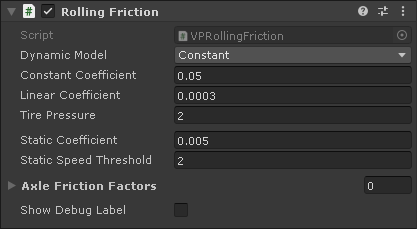
- Dynamic Model
- Model to use to calculate the rolling friction force: Constant, Linear, Tire Pressure. Each model uses the corresponding parameters as described below.
- Constant Coefficient
- In the Constant model, rolling friction is calculated as this coefficient multiplied by the vertical force.
- Linear Coefficient
- In the Linear model, rolling friction is calculated as the constant coefficient plus this coefficient multiplied by the ground speed, and the result multiplied by the vertical force.
- Tire Pressure
- In the Tire Pressure model the rolling friction force is calculated as described here. This model uses the specified tire pressure.
- Static Coefficient
- Rolling friction coefficient applied when the vehicle is stopped. This allows the vehicle to come to a stop when rolling freely on a flat surface.
- Static Speed Threshold
- Progressively apply the static coefficient to calculate the rolling friction below the specified speed.
- Axle Friction Factors
-
Optionally specify rolling friction factors to each individual axle.
For example, if the vehicle is a truck with three axles and twin wheels in the two rear axles, then you may double the rolling friction factors in these wheels by adding three elements here, one per axle:
- #0: 1 (no change in the front wheels)
- #1: 2 (double rolling friction in second axle)
- #2: 2 (double rolling friction in third axle)
- Show Debug Label
- Show debug labels with the current rolling friction forces applied to each wheel.
VPAeroSurface #
Stand-alone component (it doesn't require a VehicleBase-derived component) providing drag and downforce based on the velocity of the vehicle. The forces are applied to the vehicle at the position of the GameObject containing this component.
The recommended setup is having a VPAeroSurface GameObject at the middle of the front and rear axles. These components can configure the behavior of the vehicle at high speeds.
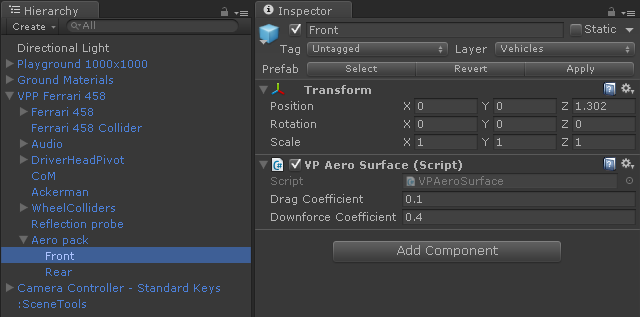
- Drag Coefficient
- Coefficient for the drag force with the speed. The force is applied counteracting the vehicle's velocity.
- Downforce Coefficient
- Coefficient for the downforce with the speed. The force is applied at the transform's position in the transform.down direction.
The force magnitudes are calculated with a simple quadratic formula:
where is the force in Newtons, is the coefficient and is the vehicle's speed in m/s.
Important:
Aerodynamic forces require keeping an eye on the suspension (you can use the Telemetry). The extra downforce will compress the suspension as well. The suspension must not reach the 100% compression (1.0) or unwanted effects will occur. Stiffer springs or progressive suspensions might be required for avoiding that.