VPWheelCollider #
This component implements the wheel colling entity in Vehicle Physics Pro:
- Suspension, steering, physical contact
- Suspension analysis in the Inspector
- Comprehensive wheel gizmo in the Scene view
- Visual meshes for wheel, brake caliper and suspension geometry
Tire friction is configured in VPVehicleController.
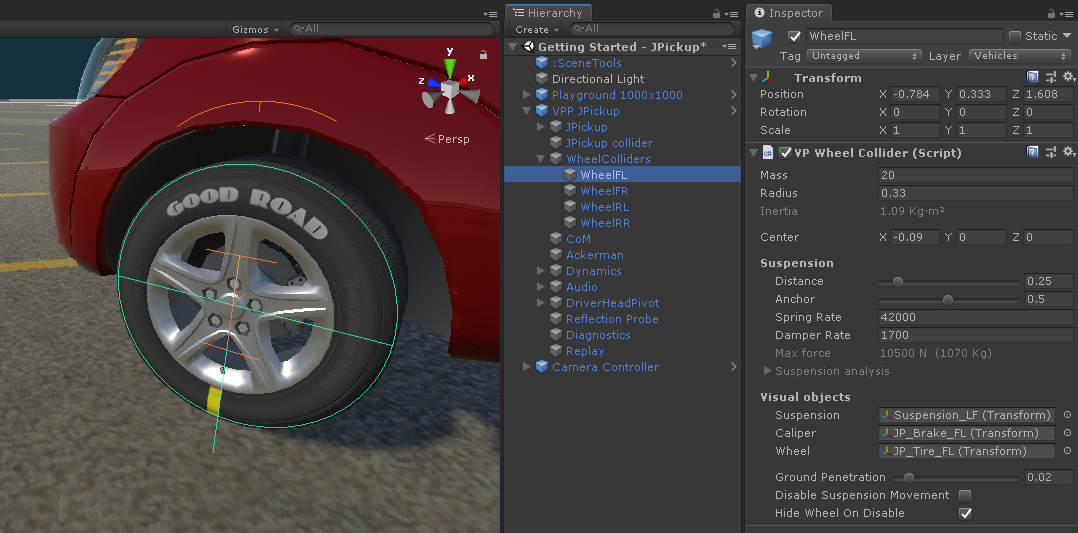
The context menu option "Adjust position and radius to the Wheel mesh" at the VPWheelCollider component automatically calculates position, radius and center to match the visual Wheel mesh specified at Visual Objects.
Mass, radius #
The mass should be roughly the mass of the wheel.
The radius should match the actual radius of the wheel mesh.
The inertia is calculated as . Note that if the inertia is too small it may have adverse effects in the numeric stability. Ensure to use a mass large enough for the wheel. Mass is used for the dynamics calculations only and doesn't have impact on the vehicle's mass.
Center #
Position offset to the center of the wheel.
The VPWheelCollider component should be placed in the same position as its corresponding visual
Wheel transform (but not in the same hierarchy, see Visual Objects below). Then
the center property is used to match the actual position of the wheel.
The best position for the wheel collider's center is the outer part of the wheel. It provides better accuracy and stability.

Suspension parameters #
- Distance (m)
- Length of the suspension travel.
- Anchor (%)
- Relative position in the suspension travel (compression) where the wheel is located at design time. This setting can be understood easily by adjusting it in the Editor and watching the gizmo in the Scene view.
- Spring rate ()
-
Springs sustain the weight of the vehicle. The inspector shows the maximum force and weight the spring can support right before hitting the limit.
Rule of thumb: a good initial value for the spring rate assumes that each suspension can support up to twice the vehicle's evenly distributed weight:
Spring Rate = vehicle mass / number of wheels * 2 * 9.81 / suspension distance - Damper rate ()
-
Dampers limit the suspension movement and damp the spring oscillations. The damper setup affects the angular momentum of the vehicle on weight shifting situations (accelerating, braking, cornering...).
Rule of thumb: a good initial value for damper rate is spring rate / 20
Dampers are very badly implemented in PhysX 3 / Unity 5. A damper value too high will surely cause weird behaviors and unnatural reactions. Learn more
Springs and dampers defaults #
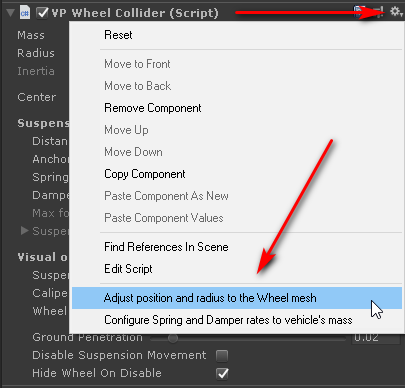
The VPWheelCollider component includes an option to configure both spring and damper using the
vehicle's mass, the number of wheels and the suspension distances:
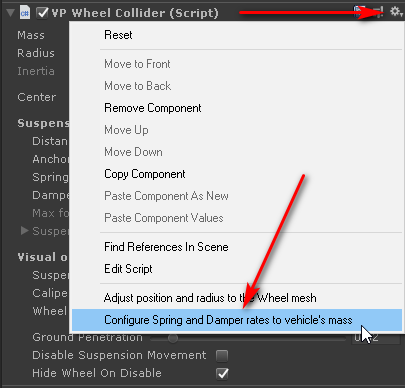
This option computes spring and damper rates using the rules above. If the vehicle's mass is evenly distributed along all wheels, then the suspension will be 50% compressed at rest.
Suspension analysis tool #
Expand the "Analysis" section under the Suspension settings of the VPWheelCollider component (select any wheel collider in your vehicle's hierarchy):
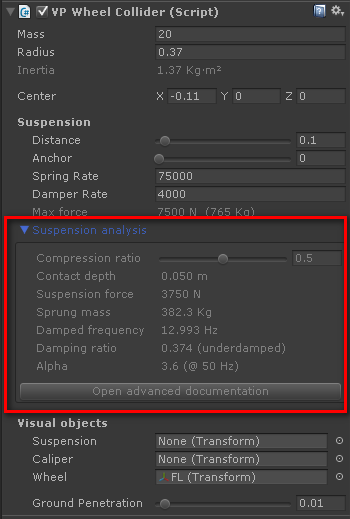
The suspension analysis tool doesn't have effect on the actual suspension behavior. It just calculates the suspension data based on the given compression ratio at rest.
- Play the scene and ensure the vehicle is at rest.
- Watch the telemetry for the compression ratio for the wheel you want to analyze.
- Specify that compression ratio in the analysis tool. It computes and shows the resulting values.
Read how suspensions work for interpreting and understanding the values.
Visual objects #
These are the transforms for the visual objects representing the actual wheel and suspension components. They will be positioned and/or rotated according to the state of the wheel.
Visual objects (Suspension, Caliper, Wheel) must reside in a different sub-hierarchy than the VPWheelColliders inside the vehicle GameObject. Read Creating Vehicles for details on how to build the vehicle hierarchy correctly.
- Suspension
- Moves vertically as for the suspension compression.
- Caliper
- Moves vertically as for the suspension compression and rotates around the Y axis as for the steering.
- Wheel
- Moves vertically as for the suspension compression, rotates around the Y axis as for the steering, and rotates around the X axis as for the wheel's angular velocity.
Suspension, Caliper and Wheel transform can be parented together in any way. They will be moved and rotated correctly.
Scripting Reference #
namespace VehiclePhysics
{
public class VPWheelCollider : VehicleBehaviour
}
Properties #
public float mass = 20.0f;
public float radius = 0.3f;
public Vector3 center;
[Range(0.01f, 2.0f)]
public float suspensionDistance = 0.25f;
// suspensionAnchor:
// The relative point in the suspension travel where the wheel is located at design time.
[Range(0,1)]
public float suspensionAnchor = 0.5f;
public float springRate = 30000.0f;
public float damperRate = 1500.0f;
public Transform suspensionTransform;
public Transform caliperTransform;
public Transform wheelTransform;
[Range(0.0f, 0.2f)]
public float groundPenetration = 0.02f;
public bool disableSuspensionMovement = false;
// Steer angle fix override. May be disabled when the forward directions of all wheels are
// pointing in the same direction as the Rigidbody.
public static bool disableSteerAngleFix = false;
// Wheel frame fix override.
// Fixes wrong calculation for WheelHit.forwardDir and WheelHit.sidewaysDir.
public static bool disableWheelReferenceFrameFix = false;
// Minimum allowed suspension distance
public static float minSuspensionDistance = 0.01f;
// Access to cachedTransform is allowed before OnEnable is invoked
public Transform cachedTransform { get; }
// Visual contact point.
// Updated at Update rate while the vehicle and the wheel are enabled.
public bool visualGrounded { get; }
public RaycastHit visualHit { get; }
// Steer angle relative to the wheel's forward direction
public float steerAngle { get; set; }
// Angular velocity and position of the visual wheel
public float angularVelocity { get; set; }
public float angularPosition { get; set; }
// Is this wheel allowed to sleep?
public bool canSleep { get; set; }
// Current spring rate being applied at the WheelCollider.
// Use for physics related calculations (i.e. force = contact depth * spring rate).
public float effectiveSpringRate { get; }
// Use for modifying suspension values in runtime
//
// These values gets reset to the component's default before each physics step.
// It may be overwritten or amended by other blocks or scripts at any criteria.
//
// Custom VehicleBehaviour components should modify these values at UpdateVehicleSuspension.
//
// NOTE: It's NOT safe reading these properties from OnEnableVehicle / OnEnableComponent
// in other component, especially when relying on the suspension values on startup.
// (i.e. as VPDynamicSuspension does). Use the regular public fields in these cases.
public float runtimeSpringRate { get; set; }
public float runtimeDamperRate { get; set; }
public float runtimeSuspensionTravel { get; set; }
// Latest suspension values that made it into the physics WheelCollider.
// Used for debug / performance charts.
public float lastRuntimeSpringRate { get; }
public float lastRuntimeDamperRate { get; }
public float lastRuntimeSuspensionTravel { get; }
// Extra downforce to be considered when computing the tire force. No other effect.
// Read from VehicleBase. Restored to 0 before each physics step.
public float runtimeExtraDownforce { get; set; }