VehicleBase reference #
VehiclePhysics.VehicleBase is the base class for every vehicle in Vehicle Physics Pro. VehicleBase
inherits from Unity's MonoBehaviour so vehicle controllers are standard components in Unity. Derived
classes implement the vehicle's internal parts by instancing, connecting and managing Block classes
(engine, gearbox, etc) in VehicleBase's overridden methods.
The standard vehicle controller in VPP, VPVehicleController, already inherits from VehicleBase. Here's an example of a custom vehicle controller with source code.
VehicleBase events #
VehicleBase events are implemented in derived classes to create the vehicle controllers.
Do NOT override OnEnable, OnDisable, Update, FixedUpdate, or LateUpdate
Always override the events provided by VehicleBehaviour instead of the MonoBehaviour's:
- OnEnable --> OnInitialize
- OnDisable --> OnFinalize
- Update or LateUpdate --> OnUpdate
- FixedUpdate --> DoUpdateBlocks or DoUpdateData
OnInitialize #
Configure the number of wheels by calling VehicleBase.SetNumberOfWheels(n). Then create, configure
and connect all your blocks. Use the Block.Connect method.
Wheels can be accessed via VehicleBase.wheels[n] and VehicleBase.wheelsState[n] after calling
SetNumberOfWheels:
wheels are the actual Wheel blocks. Required settings:
Wheel.radiusWheel.massWheel.tireFriction
wheelsState are the meaningful values of the wheels. Required settings:
WheelState.wheelColWheelState.steerable
Important: you must configure each WheelState with the corresponding WheelCollider in
WheelState.wheelCol. Also, ensure to flag the steering wheels as steerable (this is used by the
force feedback calculations).
Check out the source code example here for a comprehensive example on initializing a custom vehicle controller.
OnFinalize #
Called after the vehicle has been finalized, so the controller could finalize any custom initialization (i.e. de-subscribe to events).
DoUpdateBlocks #
Update the inputs and states for your blocks: engine, brakes, gear, etc. Called before each integration step at the physics rate (FixedUpdate rate).
DoUpdateData #
Populate the data bus with the actual values of the vehicle. Called after each integration step at the physics rate (FixedUpdate rate).
OnUpdate #
Adjust visual and per-frame stuff here at the visual refresh rate (Update rate). Frames may be skipped.
GetInternalObject #
Optional: Allow the vehicle to expose references to internal classes / blocks on demand. Each VehicleBase implementation chooses which items to expose.
This is intended for debugging / monitoring / telemetry the internal values that don't make sense to expose otherwise.
Advanced / Experimental settings #
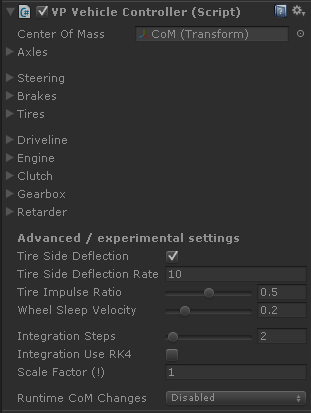
Some of these settings are likely to be changed or moved in upcoming versions. Most important are described here.
Tire side deflection #
Spring rate for the tire side to deflect and bend when sliding laterally. It can be used to simulate tires targeted to different speeds. Tires with low rates (8-20) may become difficult to drive at high speeds.
This setting will be moved to Tire Friction at some point.
Tire impulse ratio #
The default value of 0.5 works correctly on most vehicles.
- It may be raised above 0.5 on vehicles with low center of mass (e.g. F1 and racing cars) for enhancing the effect of the transition from slip to adherent.
- It should be lowered to 0.4 or less on vehicles with elevated center of mass and/or heavy load if they experiment visible jittering at rest.
Tech details
The VPP solver calculates the impulses that keep the tires adherent to the surface. These are the ideal impulses for the same vertical level as the center of mass. Tire forces are applied at a different vertical level (contact points), so these forces induce a torque in the vehicle as side effect. This torque can lead to numerical instabilities in the tire forces, being bigger with the vertical distance from the contact points to the center of mass. The tire impulse ratio prevents this effect by multiplying the calculated impulse before being applied to the vehicle as tire force.
Wheel sleep velocity #
Wheels moving slower than this speed are allowed to sleep when no other forces / torques that can move them are present.
Integration method and steps #
Substeps are subdivisions of the Unity physics time steps that are used for calculating the internal torques, forces and momentums at every block in the vehicle. The more substeps, the more precise are the numeric results but CPU usage is increased.
A minimum value of 2 substeps is recommended. Multi-driven-axle vehicles should configure at least two substeps per driven axle.
Detailed information: Solver substeps explained
Scripting Reference #
namespace VehiclePhysics
{
public abstract class VehicleBase : MonoBehaviour
}
Properties #
// Access to Wheel blocks by derived classes
protected Wheel[] wheels { get; }
// Lateral deflection of the tires
public bool tireSideDeflection = false;
public float tireSideDeflectionRate = 10.0f;
// tireImpuseRatio corrects noticeable tire force instabilities
// (enable tire force gizmos at VPTelemetry for configuring this value)
[Range(0,1)]
public float tireImpulseRatio = 0.5f;
// Wheels moving slower than this speed are allowed to sleep
[Range(0,1)]
public float wheelSleepVelocity = 0.2f;
// Enable to use the advanced (built-in) suspension damper calculations.
// Advanced damper is much more reliable, but requires a more grained configuration.
// By default (false) PhysX dampers are used (buggy).
public bool advancedSuspensionDamper = false;
// Upper limit for the damper force: vehicle mass * gravity * limit factor
// Applies when advancedSuspensionDamper is enabled.
public float suspensionDamperLimitFactor = 2.0f;
// Reduces the tire force based on the contact angle with the ground.
// Currently uses a cosine function: provides small penalty for small angles.
// This feature should be disabled on motorbikes.
public bool contactAngleAffectsTireForce = true;
// Solver substeps
[Range(1, 20)]
public int solverSubsteps = 2;
// Note: changing the CoM position at runtime causes the sprung mass values to be recomputed
// on the WheelColliders. The recalculation is also triggered when changing mass, enabling/
// disabling colliders, or changing trigger / kinematic settings.
public Transform centerOfMass;
// Set up the suspension forces to be applied at the tire contact points. This is the physically
// accurate behavior. Set to false if forceAppPointDistance needs to be adjusted externally.
[HideInInspector]
public bool accurateSuspensionForces = true;
// All wheels on the vehicle may be forced to sleep when some of the them already sleeping.
// This criteria specifies how to decide when the sleep mode should be forced in all wheels.
//
// - Strict: works on most vehicles (half of the wheels sleeping force all others to sleep as well).
// - Relaxed: may be required on some special types of vehicles, such as track-based vehicles.
// These special vehicles may refuse to move even when applying power to their wheels
// due to the vehicle sleep criteria.
//
// You shouldn't need to modify this unless you're writing your own VehicleBase-derived
// controller.
public enum VehicleSleepCriteria { Strict, Relaxed };
[HideInInspector]
public VehicleSleepCriteria vehicleSleepCriteria = VehicleSleepCriteria.Strict;
// Prevents the wheels to sleep the next physics frame only.
[NonSerialized]
public bool inhibitWheelSleep = false;
// Visually inverts the spin direction of the wheels next visual frame only.
// No effects on the physics, only in the visual wheel transform.
// This is typically used for reverse replays.
[NonSerialized]
public bool invertVisualWheelSpinDirection = false;
// Cached transform and rigidbody.
// Access is allowed before OnEnable is invoked.
public Transform cachedTransform { get; }
public Rigidbody cachedRigidbody { get; }
// Is this vehicle completely initialized?
[DefaultValue(false)]
public bool initialized { get; }
// Public access to the ground material manager used by this vehicle for retrieving
// GroundMaterials. It can be set at OnInitialize, or the scene will be searched for a
// GroundMaterialManagerBase-derived component. It can also be set anytime at runtime.
public GroundMaterialManagerBase groundMaterialManager { get; set; }
// Public access to the vehicle data bus
public DataBus data = new DataBus();
// Public shortcut to wheel count
public int wheelCount { get; }
// Public access to wheel states
public WheelState[] wheelState { get; }
// Public access to speed and speed angle (m/s and degrees, respectively)
public float speed { get; }
public float speedAngle { get; }
// Public access to the local accelerations
public Vector3 localAcceleration { get; }
public Vector3 localAngularAcceleration { get; }
// Public Pause feature
//
// Equivalent to disabling the component, but the internal state is preserved.
// Note that only pauses the internal updates. The Physics rigidbody and friction-less
// WheelColliders keep operating normally.
//
// Pause is currently designed to be used by other components (replay, pause vehicle...)
public bool paused { get; set; }
Events #
// Exposed events occurring at several stages of the vehicle simulation. Advanced use only.
// These events may have any number of subscribers (i.e. from VehicleBehaviour-based add-ons).
public Action onPreDynamicsStep; // Invoked before computing each dynamics step
public Action onBeforeUpdateBlocks; // Invoked before calling DoUpdateBlocks
public Action onBeforeIntegrationStep; // Invoked before the solver integration
public Action onDynamicsStepCompleted; // Invoked after each dynamics step is completed
public Action onPreVisualUpdate; // Invoked before updating visual stuff
Nested classes #
// State of each wheel in the vehicle
public class WheelState
{
public int wheelIndex; // Index of this wheel within the vehicle
// Associated VPWheelCollider ----------------------------------------------------
public VPWheelCollider wheelCol;
public bool steerable = false;
// External input ----------------------------------------------------
public float steerAngle;
// Collider state ----------------------------------------------------
public bool grounded = false; // Physics contact point (FixedUpdate)
public WheelHit hit;
// Contacted ground material
public GroundMaterial groundMaterial;
public GroundMaterialHit lastGroundHit;
public float linearGroundPosition;
// Suspension state
public float contactDepth; // Depth of the suspension compression (m)
public float suspensionCompression; // Compression ratio: 0.0 = fully elongated, 1.0 = 100% compressed
public float suspensionLoad; // Total vertical load supported by the suspension and applied on the wheel
public float verticalForce; // Amount of the vertical load that is directly applied on the contact patch. May be translated to friction force.
public float normalizedLoad; // Load for each tire relative to vehicle weight, normalized to 1 = rest in an evenly balanced car, 0 = in air
public float contactAngle; // Angle of the wheel with the surface (wheel's forward direction)
public float contactSpeed; // Speed of movement of the suspension. Used for calculating the damper.
public float damperForce; // Damper force applied
public float lastContactDepth; // Contact depth from the previous step (for contact speed)
// Local reference frame (from Hit)
public Vector3 wheelVelocity; // Surface tangent velocity (forward-right plane)
public Vector3 surfaceForce; // Force canceling surface slope in steady state
public Vector2 localWheelVelocity; // The above translated to the forwards-sideways local frame (y,x)
public Vector2 localSurfaceForce; // (hit.forwardDir, hit.sidewaysDir).
public Vector2 externalTireForce; // Local forces canceling the tire's sliding velocity over the surface
// Integrated data (from the Solver) ----------------------------------------------------
public float angularVelocity; // Angular velocity (spin)
public Vector2 tireForce; // Tire force at the contact point
public float reactionTorque; // Reaction torque
public Vector2 tireSlip; // Tire slip in m/s
public float combinedTireSlip; // Combined tire slip magnitude, in m/s (for tire effects)
public Vector2 lastTireForce; // Tire force from the previous step (for tire deflection)
// Torques at the axle from the previous step
public float driveTorque;
public float brakeTorque;
}
// State variables for the vehicle and each wheel
public struct VehicleStateVars
{
public float time;
public Vector3 lastVelocity;
public float lastImpactTime;
}
public struct WheelStateVars
{
public float L;
public float Tr;
public float contactDepth;
public Vector2 lastTireForce;
}
// State of the internal solver
public struct BlockState
{
public float L;
public float I;
public float Tr;
public float Td;
}
public struct SolverState
{
public int step;
public float time;
public BlockState[] blockStates;
}
Methods #
// Derived classes must call SetNumberOfWheels for declaring the number of wheels for this vehicle
protected void SetNumberOfWheels (int numberOfWheels)
// Utility method for calculating the local position of a wheel with respect to the
// main vehicle's body.
public Vector3 GetWheelLocalPosition (VPWheelCollider wheelCol)
// Methods dealing with object's colliders.
//
// This procedure ensures that visual wheels don't collide with own vehicle's colliders, causing
// undesired visual artifacts. Vehicle's colliders are temporarily moved to the "Ignore Raycast"
// layer before throwing the rays, and restored afterwards.
//
// NotifyCollidersChanged should be called whenever colliders are added or removed to the
// rigidbody. No need to call this method when colliders are enabled, disabled or their layer
// changes.
public void NotifyCollidersChanged ()
public Collider[] GetVehicleColliders (bool includeInactive)
// Update the dynamics a single step while the vehicle is paused (paused = true)
public void SingleStep ()
// Teleports the vehicle to a new position.
// VehicleBehaviours are notified.
public void Reposition (Vector3 position, Quaternion rotation)
// Methods for interacting with the wheels.
// Use GetWheelIndex for accessing wheel by axle / position.
// Modify the radius of a wheel
//
// This is intended for simulating tire pressure or puncture, so the change does not
// modify the wheel's inertia.
//
// NOTE:
// The radius is also modified at the VPWheelCollider component, so disabling/re-enabling
// the vehicle will cause the inertia to be recalculated using the modified radius.
// It's advised to backup the previous radius (GetWheelRadius) and restoring it
// when disabling the vehicle (e.g. at VehicleBehaviour.OnDisableVehicle).
public void SetWheelRadius (int wheelIndex, float radius)
// Return the radius of the wheel as seen from the vehicle dynamics.
public float GetWheelRadius (int wheelIndex)
// Modify the tire friction of a wheel
//
// The original friction is restored when the vehicle is disabled and reenabled.
public void SetWheelTireFriction (int wheelIndex, TireFriction friction)
// Return the tire friction object used by a wheel
public TireFriction GetWheelTireFriction (int wheelIndex)
// Apply a multiplier to the friction of the tire
public void SetWheelTireFrictionMultiplier (int wheelIndex, float frictionMultiplier)
// Return the angular velocity that produces a specific slip in a given wheel
public float GetWheelAngularVelocityForSlip (int wheelIndex, float slip)
// Return the wheel's peak slip in m/s
public Vector2 GetWheelPeakSlip (int wheelIndex)
// Return the wheel's maximum adherent slip in m/s
public Vector2 GetWheelAdherentSlip (int wheelIndex)
// Apply brakes to some specific wheel the next frame.
// Torque is accumulated to any other torque coming from other components (i.e. brakes, ESP).
public void AddWheelBrakeTorque (int wheelIndex, float torque)
// Get and restore the state vars for the vehicle and wheels
public VehicleStateVars GetVehicleStateVars ()
public void SetVehicleStateVars (VehicleStateVars stateVars)
public WheelStateVars[] GetWheelStateVars ()
public void SetWheelStateVars (WheelStateVars[] stateVars)
// Get the state of the internal solver.
// Use for debug or development diagnostics only.
public SolverState GetSolverState ()
public Type[] GetSolverBlockTypes ()
// Utility methods: Log messages to Unity's console including component and gameobject information
public void DebugLogWarning (string message)
public void DebugLogError (string message)
Virtual methods #
// Configure the number of wheels (SetNumberOfWheels, wheels[], wheelsState[]).
// Create, configure and connect all the vehicle's blocks (Block.Connect).
protected virtual void OnInitialize ()
// Called after the vehicle has been finalized, so the controller could
// finalize any custom initialization (i.e. de-subscribe to events)
protected virtual void OnFinalize ()
// Update the values and inputs for your blocks: engine, brakes, gear, etc.
// Called before each integration step (FixedUpdate rate).
protected virtual void DoUpdateBlocks ()
// Populate the data bus with the actual values of the vehicle.
// Called after each integration step (FixedUpdate rate).
protected virtual void DoUpdateData ()
// Adjust visual and per-frame stuff here (Update rate).
// Called at the end of Update.
protected virtual void OnUpdate ()
// Allow the vehicle to expose references to internal classes / blocks on demand.
// Each vehicle implementation chooses which items to expose.
public virtual object GetInternalObject (Type type)
// Default vehicle implementation assumes 2 wheels on each axle.
// Override this if the vehicle has a different or variable number of wheels per axle.
public enum WheelPos { Default = 0, Left = 0, Right = 99 };
public virtual int GetWheelIndex (int axle, WheelPos position = WheelPos.Default)
public virtual int GetAxleCount ()
See also #
Block
GroundMaterial
GroundMaterialHit
GroundMaterialManagerBase
TireFriction
VehicleBehaviour
VPWheelCollider
Wheel
Contact Processing Reference #
Properties #
// Contact processing may be disabled for performance by setting disableContactProcessing = true.
public bool showContactGizmos = true;
[HideInInspector]
public bool disableContactProcessing = false;
public static VehicleBase vehicle = null;
public static Collision currentCollision = null;
public static bool isCollisionEnter = false;
// Impact properties. Use from an OnImpact event only.
// Values get massaged properly just before invoking the event.
public Vector3 localImpactPosition { get; }
public Vector3 localImpactVelocity { get; }
public bool isHardImpact { get; }
// Body drag properties. May be queued every frame.
public Vector3 localDragPosition { get; }
public Vector3 localDragVelocity { get; }
public bool isHardDrag { get; }
public Collider lastContactedCollider { get; }
[NonSerialized]
public float impactThreeshold = 0.6f; // 0.0 - 1.0. The DotNormal of the impact is calculated. Less than this value means drag, more means impact.
[NonSerialized]
public float impactInterval = 0.2f; // Time interval between processing impacts for visual or sound effects.
[NonSerialized]
public float impactIntervalRandom = 0.4f; // Random percentaje for the impact interval, avoiding regularities.
[NonSerialized]
public float impactMinSpeed = 2.0f; // Minimum relative velocity (m/s) at which conctacts may be consideered impacts.
Events #
public Action onImpact; // Invoked when the impact information has been updated
public Action onRawCollision; // Raw subscription to OnCollisionEnter and OnCollisionStay