Ground Materials #
VPGroundMaterialManager #
Manages the different ground materials in the scene associating each one with an Unity PhysicMaterial.
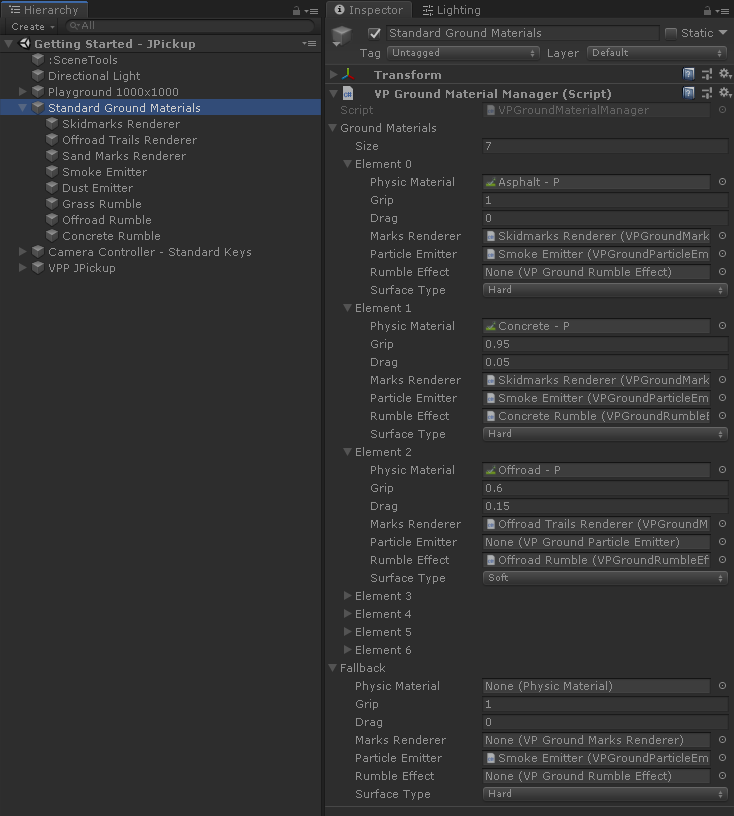
A GameObject with a VPGroundMaterialManager component should be available at the scene for the
vehicles to use the properties of the ground materials. Vehicles may also receive a ground material
manager later by setting their VehicleBase.groundMaterialManager property.
When a wheel of a vehicle touches any non-trigger collider it queries the VPGroundMaterialManager
instance passing the PhysicMaterial of the touched collider (it may be null if the collider has no
physic material assigned). The Ground Material Manager looks up the physic material in its
Ground Materials list and returns the first GroundMaterial object that matches the given
physic material. If no match is found then the Fallback material is returned.
Note that None is also valid as physic material for identifying a ground material. This would match the colliders without physic material assigned.
Loading scenes and objects from asset bundles
Unity asset bundles store copies of the physic materials. When the bundle loaded, the physic materials are loaded as new instances, not references to the original. Thus, a GroundMaterialManager existing in the scene wouldn't recognize those materials.
Possible solutions:
- Include the VPGroundMaterialManager object in the bundle, so references to the physic materials are preserved.
- Explicitly fix the references to the physic materials in the colliders after loading the bundle. You may compare by name and assign a correct reference so the physic materials can be found in the GroundMaterialManager list.
- Write your own ground material manager derived from GroundMaterialManagerBase. Assign the ground materials based on the physic material's name instead of the reference.
GroundMaterial #
The class VehiclePhysics.GroundMaterial holds the data and objects associates to a specific ground
material. The Ground Materials are defined and managed at the VPGroundMaterialManager component.
Ground Materials are used by the vehicle and its add-ons.
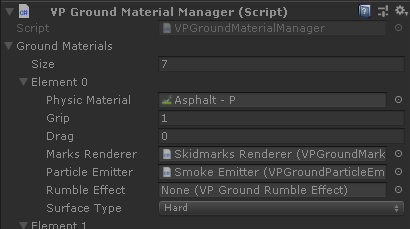
- Physic Material
-
The Unity physic material associated to this ground material. Used for finding the Ground Material when wheel hits a collider with that physic material assigned. None is also valid for identifying colliders without physic material assigned.
The values of the Physic Material itself (Static Friction, Dynamic Friction, etc) do NOT have any effect in the tire friction. Only Grip and Drag below affect the tire forces.
- Grip
-
Grip multiplier of the surface. Some reference examples are:
Surface Grip Dry tarmac 1 Wet tarmac 0.82 Snow 0.3 Ice 0.1 - Drag
-
Drag coefficient. Produces a drag force based on the speed and load of the wheel on the surface. The formula used for computing the drag force is:
where:
- is the drag force in Newtons
- is the drag coefficient
- is the downforce in Kilonewtons (KN, newtons * 0.001)
- is the velocity of the wheel over the surface in m/s
- Marks Renderer
- Optional reference to a VPGroundMarksRenderer component for drawing the tire marks on this ground material. Marks will be triggered by the component VPTireEffects if available in the vehicle.
- Particle Emitter
- Optional reference to a VPGroundParticleEmitter component for emitting particles on this ground material. Particles will be triggered by the component VPTireEffects if available in the vehicle.
- Rumble Effect
- Optional reference to a VPGroundRumbleEffect component for simulating rumble and ground relief in the wheels without depending on the collision geometry.
- Surface Type
-
A hint on the type of surface. Mostly used by vehicle add-on components such as VPAudio for playing different effects:
- Hard: tire skid audio, hard impacts, hard body drag, body scratches (asphalt, tarmac, concrete, metal...)
- Soft: offroad rumble audio, soft impacts, soft body drag (offroad, mud, grass, sand, gravel...)
- Neutral: no tire nor rumble audio, hard impacts, hard body drag, body scratches (ice)
VPGroundMarksRenderer #
Dynamically creates and renders the marks over the ground.
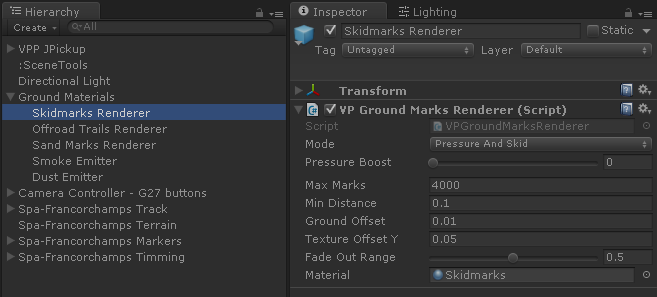
Each type of marks is generated by a VPGroundMarksRenderer component bound to one or several Ground Materials. The component VPGroundMaterialManager manages all the Ground Materials and Ground Mark Renderers in the scene.
- Mode
-
Conditions that trigger the tire marks:
-
Pressure And Skid: marks are generated when tire is skidding over the surface. The intensity of the marks depend on the vertical force (pressure) and the slip velocity. Example: typical skid marks on tarmac.
-
Pressure Only: marks are generated always when the tire is touching the surface. The intensity of the marks depend on the vertical force (pressure) only. Example: tire marks on mud.
-
- Pressure Boost
- Intensification of the marks with pressure.
- Max Marks
-
Maximum number of mark segments the renderer will handle. Old marks will be faded out progressively according to the Fade Out Range parameter.
The number of marks has direct influence on the performance. The entire mesh with the marks needs to be processed each time new segments are added.
- Min Distance
- Minimum distance among two consecutive tire marks.
- Ground Offset
- Distance over the surface the marks are generated at. Increase if Z-fighting problems are observed among the marks and the surface.
- Texture Offset Y
- Offset in the vertical direction the marks texture is clamped at. This improves the visual continuity of marks when the texture don't fully wraps around on the V coordinate.
- Fade Out Range
- Proportion of the old marks that will be progressively faded out when new marks are generated.
- Material
- The Mesh Renderer for the marks will use this Material when creating it in runtime. It won't be used if a Mesh Renderer is provided in edit time.
VPGroundParticleEmitter #
Controls an Unity Particle System for creating the particle effects over the ground. Requires a Particle System component and a material for the particles.
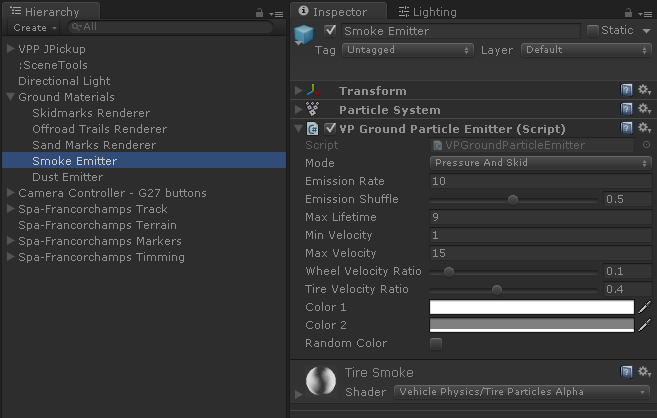
Each type of particle effect is generated by a pair VPGroundParticleEmitter - ParticleSystem. The VPGroundParticleEmitter component is bound to one or several Ground Materials. The component VPGroundMaterialManager manages all the Ground Materials and Ground Particle Emitters in the scene.
- Mode
-
Conditions that trigger the particle effect:
- Pressure And Skid: the tire skidding over the surface triggers the particle effect. The intensity of the effect depends on the vertical force (pressure) and the slip velocity. Example: tire smoke on burnouts.
- Pressure And Velocity: the wheel moving on the surface triggers the particle effect. The intensity of the effect depends on the vertical force (pressure) and the speed. Example: dust clouds on sand.
- Emission Rate
- Rate at which the particles are emitted.
- Emission Shuffle
- Randomness ratio on the emission rate.
- Max Lifetime
- Maximum lifetime of each particle.
- Min Velocity, Max Velocity
- Velocity range for applying intensity to the effect in the Pressure And Velocity mode.
- Wheel Velocity Ratio
- How much of the velocity of movement of the wheel is applied to the particle.
- Tire Velocity Ratio
- How much of the tire velocity over the ground (slip) is applied to the particle.
- Color 1
- Tint color for the particles.
- RandomColor, Color 2
- If RandomColor is checked, a random color in the range Color1 - Color2 will be applied to each new particle.
VPGroundRumbleEffect #
Implements rumble effects for ground materials (kerbs, offroad, etc) by applying vertical rumble forces at the wheel contact point. The component simulates "virtual bumps" and applies forces to the car pretending the wheel is driving over them.
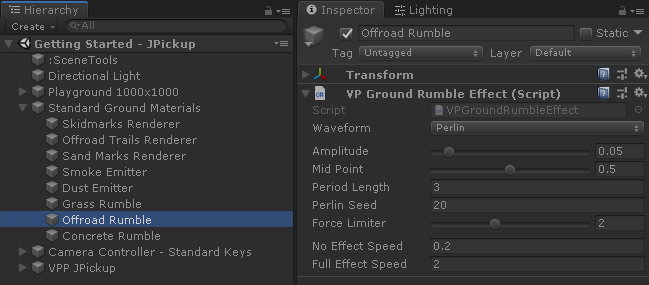
Each type of rumble effect is generated by a VPGroundRumbleEffect component bound to one or several Ground Materials. The component VPGroundMaterialManager manages all the Ground Materials and Ground Rumble Effects in the scene.
- Wafeform
-
The shape of the "virtual bumps" when the wheel drives over them.
- Triangle. Linear up and linear down.
- Saw. Linear up, then step down.
- Perlin. Uses Unity's Mathf.PerlinNoise for simulating pseudo-random smooth irregularities.
- Step. Step up. Just raises the wheel while driving on this effect.
Triangle and Saw are good for ribbed kerbs or "rumble strips" in racing circuits.
Perlin is good for general irregularities. Offroad and grass have a lower period length (= higher frequency), while road and track surfaces may use a larger period length (= lower frequency).
Step may be used for road sidewalks or non-ribbed kerbs in racing circuits.
- Amplitude
- The total height (m) of the "virtual bumps", from the lowest to the highest point.
- Mid Point
-
Where to locate the mid point of the bump height. For example, if Amplitude is 0.10 (10 cm):
- 0.0: base of the bump at surface level, then bumps are 10 cm height.
- 0.5: bump sinks 5 cm to the surface, and raises other 5 cm.
- 1.0: bump sinks 10 cm to the surface, with the higher part at surface level.
- Period Length
-
Length in m of a single cycle in the waveform:
- Triangle: length between each valley or peak.
- Saw: length between each peak.
- Perlin: length of a normalized perlin coordinate.
- Step: no effect.
- Perlin Seed
- Seed to the perlin randomness. Will be used as coordinate X in the call to Mathf.PerlinNoise.
- Force Limiter
- Factor that limits the magnitude of the force to apply, as multiplier of the current vertical suspension force. More force allows to raise the wheel more, but also may produce unexpected effects.
- No Effect Speed
- The ground rumble effect is canceled below this speed (m/s).
- Full Effect Speed
- The effect is fully applied above this speed (m/s). Bellow this speed the effect is faded to cancellation at No Effect Speed.
Custom Ground Materials #
By inheriting from GroundMaterialManagerBase you could write your own Ground Material Manager
component that provides VPP vehicles with the ground properties based on your own criteria.
GroundMaterialManagerBase.GetGroundMaterial receives the information on the contact in
GroundMaterialHit, including contacted collider, physics material and contact point. The
method then returns a GroundMaterial instance with the ground properties (grip, drag,
effects...).
Once you've written your custom Ground Material Manager component, simply add it to some GameObject
in the scene and ensure to disable or remove the stock VPGroundMaterialManager. VPP Vehicles
will find and use your component automatically.
See the comments in the code below for more details.
Scripting Reference #
GroundMaterial.cs #
using UnityEngine;
using System;
namespace VehiclePhysics
{
[Serializable]
public class GroundMaterial
{
// Unity PhysicMaterial this ground material is bound to
public PhysicMaterial physicMaterial;
// Grip multiplies the tire friction on this material.
// Drag applies a force that opposes the movement. It's based on the downforce in kN:
//
// dragForce = downforce * 0.001 * drag * velocity^2
public float grip = 1.0f;
public float drag = 0.0f;
// Wheel effects triggered when driving on this ground material.
public VPGroundMarksRenderer marksRenderer;
public VPGroundParticleEmitter particleEmitter;
public VPGroundRumbleEffect rumbleEffect;
// Surface type affects the audio clips and other effects that are invoked
// depending on the surface. See the VPAudio component.
//
// Hard: tire skid audio, hard impacts, hard body drag, body scratches (i.e. asphalt)
// Soft: offroad rumble, soft impacts, soft body drag (i.e. offroad)
// Neutral: no tire nor rumble audio, hard impacts, hard body drag, body scratches (i.e. ice)
public enum SurfaceType { Hard, Soft, Neutral };
// Custom pointer to be used from scripting when you need to reference additional
// data per ground material in your own custom ground material manager.
// Thus, you would be able to access this data from your own scripts.
// This field won't appear in the inspector.
public object customData = null;
}
public struct GroundMaterialHit
{
// Physic material to find a GroundMaterial for. May be null.
public PhysicMaterial physicMaterial;
// The Collider that was hit.
public Collider collider;
// World position of the contact point.
public Vector3 hitPoint;
}
// Base class for the components that host and manage the materials for the scene.
//
// When a vehicle is initialized it will search for the first instance of a
// GroundMaterialManagerBase-derived class. A ground material manager may also be assigned
// explicitly to a vehicle via VehicleBase.groundMaterialManager property.
public abstract class GroundMaterialManagerBase : MonoBehaviour
{
// GetGroundMaterial must return a GroundMaterial object for the given GroundMaterialHit
// and vehicle.
//
// vehicle VehicleBase object which is querying the material.
// groundHit Contact information
//
// returns A non-null GroundMaterial reference
public abstract GroundMaterial GetGroundMaterial (VehicleBase vehicle, GroundMaterialHit groundHit);
// Update a GroundMaterial reference by invoking GetGroundMaterial only if the cached physic
// material has changed. Vehicles call this method for retrieving the ground material per wheel
// on each physics frame.
//
// vehicle VehicleBase object which is querying the material.
// groundHit Contact information.
// cachedGroundHit Reference to the cached contact information. Will be updated when necessary.
// groundMaterial Reference to the ground material. Will be updated only when the physic
// material changes.
public virtual void GetGroundMaterialCached (VehicleBase vehicle, GroundMaterialHit groundHit,
ref GroundMaterialHit cachedGroundHit, ref GroundMaterial groundMaterial)
{
// Query the ground material (typically slow, table look-up) only when the physic material changes.
// Otherwise do not change actual ground material reference.
//
// NOTE: This default implementation verifies the physic material only. collider and hitPoint
// are ignored. This method must be overridden with a proper implementation if the
// GetGroundMaterial implementation uses collider and/or hitPoint.
if (groundHit.physicMaterial != cachedGroundHit.physicMaterial)
{
cachedGroundHit = groundHit;
groundMaterial = GetGroundMaterial(vehicle, groundHit);
}
}
}
}
VPGroundMaterialManager.cs #
using UnityEngine;
namespace VehiclePhysics
{
[AddComponentMenu("Vehicle Physics/Ground Materials/Ground Material Manager")]
public class VPGroundMaterialManager : GroundMaterialManagerBase
{
public GroundMaterial[] groundMaterials = new GroundMaterial[0];
public GroundMaterial fallback = new GroundMaterial();
// Returns a GroundMaterial from the list based on the given PhysicMaterial.
// null is also valid as physic material (colliders with no physic material assigned).
// vehicle VehicleBase object which is querying the material
// groundHit Contact information (physic material, collider, position)
//
// returns A GroundMaterial from the list, or the fallback material if no matching
// PhysicMaterial is found
public override GroundMaterial GetGroundMaterial (VehicleBase vehicle, GroundMaterialHit groundHit)
{
for (int i=0, c=groundMaterials.Length; i<c; i++)
{
if (groundMaterials[i].physicMaterial == groundHit.physicMaterial)
return groundMaterials[i];
}
return fallback;
}
}
}